Configuring direct media connection¶
A direct media connection is often referred to as Open RTP (ORTP).
Perform the following configuration on the originator and terminator:
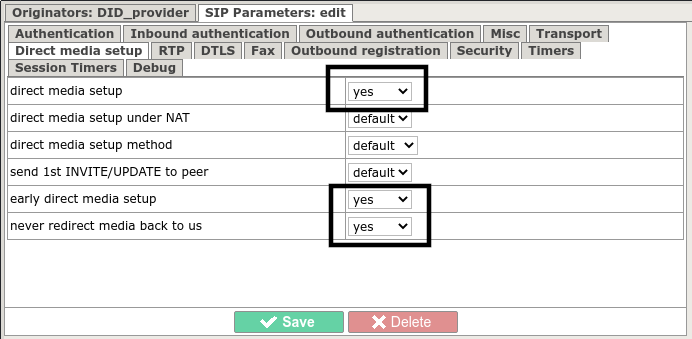
A direct media connection will only be active if both peers involved in the call have these settings.
Also, the following conditions must be met:
- both peers must have identical codecs
- audio recording must be disabled
- if RFC2833 mode is used for DTMF transmission (DTMF in RTP stream), then DTMF-dependent functions must be disabled (See VAS).
If you need to configure a direct RTP connection for part of the traffic from the client, then you need to configure several originators with the above settings for the client.
You can divide the traffic between originators by the B-number prefix.
At the same time, the above settings must be enabled on each originator for such a client (even for those originators for which you do not need to perform a direct media connection).
Through Route classes you will need to route calls to the appropriate terminators.
Since direct media connection only works if the above settings are enabled for both originator and terminator, by selecting a terminator in the Route Class you will control the activation of this feature.
If the same terminator must process both ORTP traffic and non-ORTP traffic, then you need to add 2 terminators.
Name one terminator "VendorName" and configure it without ORTP.
Name the second terminator "VendorName_ORTP" and configure it with ORTP.
Through Route classes you will need to route calls to the appropriate terminators.
If the originator and the terminator had different sets of supported codecs established during the call, then theoretically the call can go in any of these codecs,
making different codecs selected on originator and terminator, which means ORTP may not work.
Therefore, it is advisable to enable "RTP -> preferred codec only" on the ORTP originator and ORTP terminator, so that the system selects only 1 codec for a call, and does not offer a set of codecs to peers:
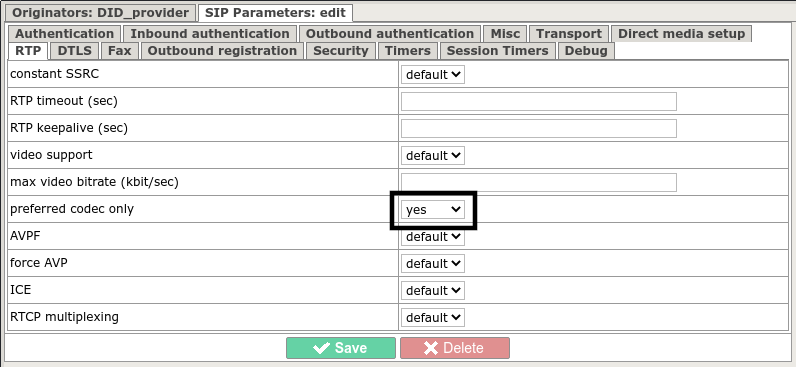
See the Codec translation section for details.